Check out today’s Step 1 Qmax Question Challenge.
Know the answer? Post it below! Don’t forget to check back for an update with the correct answer and explanation (we’ll post it in the comments section below).
A 45-year-old woman presents with a complaint of difficulty sleeping two to three times per week because of wheezing. She is currently taking albuterol by metered-dose inhaler. She is placed on a medication that stabilizes the type of cells pictured in the image.
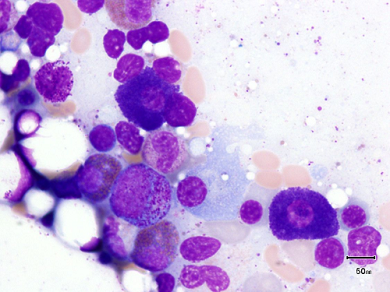
Which medication was she prescribed?
A. Cromolyn sodium
B. Ipratropium bromide
C. Montelukast
D. Salmeterol
E. Theophylline
———————–
Want to know the ‘bottom line?’ Purchase a USMLE-Rx Subscription and get many more features, more questions, and passages from First Aid, including images, references, and other facts relevant to this question.
This practice question is an actual question from the USMLE-Rx Step 1 test bank. For more USMLE Step 1 prep, subscribe to our Flash Facts and Step 1 Express video series. Score the best deal on all three products with a Step 1 Triple Play Bundle.



A. Cromolyn sulfate stabilizes mast cells, used in Asthma treatment
A. Cromolyn sodium
The correct answer is A. The cells with many granules, indicated by red circles in the image, are mast cells. Cromolyn works at the surface of mast cells to inhibit their degranulation. This, in turn, prevents the release of histamine and slow-reacting substance of anaphylaxis, mediators of type I allergic reactions. Cromolyn may also reduce the release of inflammatory leukotrienes.
B is not correct. Antimuscarinics (ie, ipratropium bromide) cause vagolytic action by competitive inhibition of muscarinic receptors on airway smooth muscle (M3 type), leading to bronchodilation. They have no effect on mast cell activity.
C is not correct. Leukotriene antagonists (eg, montelukast) act as competitive antagonists of leukotriene (CysLT1) receptors.
D is not correct. ?2-Adrenoceptor agonists (eg, albuterol and salmeterol) stimulate airway ?2 adrenoceptors. This causes relaxation of bronchial smooth muscle.
E is not correct. Methylxanthines (eg, theophylline) cause relaxation of bronchial smooth muscle by phosphodiesterase inhibition.