Check out today’s Step 1 Qmax Question Challenge.
Know the answer? Post it below! Don’t forget to check back for an update with the correct answer and explanation (we’ll post it in the comments section below).
 A 57-year-old man has arthritis, which is treated with a cycloocygenase (COX)-2 inhibitor. He presents to the emergency department with sudden-onset shortness of breath and chest pain which radiates to his jaw and left arm.
A 57-year-old man has arthritis, which is treated with a cycloocygenase (COX)-2 inhibitor. He presents to the emergency department with sudden-onset shortness of breath and chest pain which radiates to his jaw and left arm.
Which of the following best explains why the patient may have been better off using aspirin for his arthritis instead of selective COX-2 inhibitors?
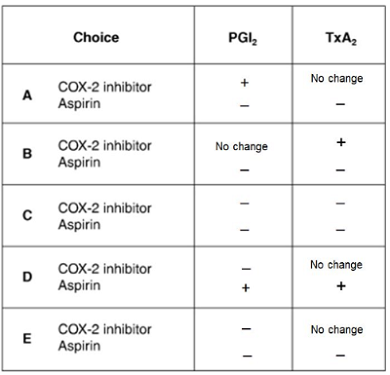
KEY: (+ denotes an in increase in concentration and – denotes a decrease in concentration, PGI2 = prostaglandin I2, TxA2 = thromboxane A2)
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. E
———————–
Want to know the ‘bottom line?’ Purchase a USMLE-Rx Subscription and get many more features, more questions, and passages from First Aid, including images, references, and other facts relevant to this question.
This practice question is an actual question from the USMLE-Rx Step 1 Qmax test bank. For more USMLE Step 1 prep, subscribe to our First Aid Step 1 Flash Facts and First Aid Step 1 Express Videos video series. Score the best deal on all three products as a bundle with USMLE-Rx 360 Step 1.




A thromboxane A2 (TXA2) and prostacyclin (PGI2) . These hormones are labile metabolites of arachidonic acid. TXA2 is generated by blood platelets, while PGI2 is produced by vascular endothelium. TXA2 is a potent vasoconstrictor. It also initiates the release reaction, followed by platelet aggregation. PGI2 is a vasodilator, especially potent in coronary circulation. It also inhibits platelet aggregation by virtue of stimulation of platelet adenyl cyclase. A balance between formation and release of PGI2, TXA2 and/or cyclic endoperoxides in circulation is of utmost importance for the control of intra-arterial thrombi formation and possibly plays a role in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis.
E)
The probable diagnosis is drug-induced mi
Arachidonic Acid ——-COX-1—-> TXA2
Arachidonic Acid ——-COX-2—-> PGI2
Selective COX-2 inhibitors would decrease PGI2 and thus increase risk for vasoconstriction and platelet aggregation without affecting levels of TXA2.
Nonselective COX inhibitor (ASPIRIN) inhibits production of both TXA2 & PGI2 in earlier stage.
B, ASA inhibits both COX, so we can rule out D. selective COX2 inhibitor increases risk of MI. How? In the arachidonic acid pathway they inhibit the production of PGE-2 that causes fever and pain. Substrate accumulates, all that substrates goes to he other side of the pathway stimulating the production of tromboxane A2 that is platelet agregating substance.
agree with B