Check out today’s Step 1 Qmax Question Challenge.
Know the answer? Post it below! Don’t forget to check back for an update with the correct answer and explanation (we’ll post it in the comments section below).
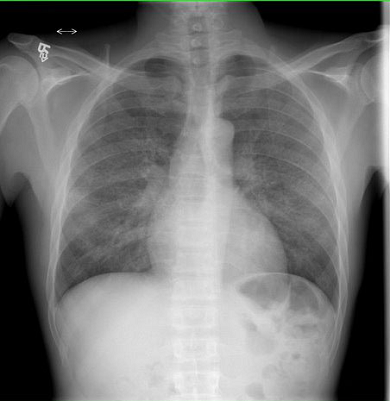 A 40-year-old patient with AIDS presents to the clinic with fatigue and weakness. X-ray of the chest is shown in the image. A methenamine silver stain of a bronchoalveolar lavage specimen reveals multiple organisms. Treatment with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole is contraindicated because the patient has a sulfa allergy.
A 40-year-old patient with AIDS presents to the clinic with fatigue and weakness. X-ray of the chest is shown in the image. A methenamine silver stain of a bronchoalveolar lavage specimen reveals multiple organisms. Treatment with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole is contraindicated because the patient has a sulfa allergy.
Which of the following agents should be used to treat this patient’s infection?
A. Penicillin
B. Pentamidine
C. Ivermectin
D. Metronidazole
E. Protamine
———————–
Want to know the ‘bottom line?’ Purchase a USMLE-Rx Subscription and get many more features, more questions, and passages from First Aid, including images, references, and other facts relevant to this question.
This practice question is an actual question from the USMLE-Rx Step 1 test bank. For more USMLE Step 1 prep, subscribe to our Flash Facts and Step 1 Express video series. Score the best deal on all three products with USMLE-Rx 360 Step 1.




B
B
Pentamidine
B
B)
PCP
The correct answer is B. The diffuse hazy “groundglass” opacities and interstitial infiltrate seen on this chest x-ray are consistent with Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia, which is confirmed by methenamine silver stain of sample (typically bronchoalveolar lavage, but sometimes induced sputum or or biopsy samples). The first-line treatment of this condition is trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole for patients with no contraindications to sulfa drugs. In the case of a patient with a sulfa allergy, the first-line treatment is pentamidine.
A is not correct. Penicillin is used to treat a variety of bacterial infections but is not effective in the treatment of Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia.
C is not correct. Ivermectin is used to treat onchocerciasis (river blindness). It is thought to block the release of microfilariae from gravid female worms. One dose reduces microfilarial counts by up to 95%.
D is not correct. Metronidazole is used to treat a wide variety of anaerobic bacterial infections. It is also effective against parasitic infections such as Giardia lamblia, Entamoeba histolytica, Gardnerella vaginalis, and Trichomonas vaginalis.
E is not correct. Protamine is used to treat heparin overdose. It binds to heparin to form a stable complex that has no anticoagulant activity. Used alone, protamine has anticoagulant properties.