Check out today’s Step 1 Qmax Question Challenge.
Know the answer? Post it below! Don’t forget to check back for an update with the correct answer and explanation (we’ll post it in the comments section below).
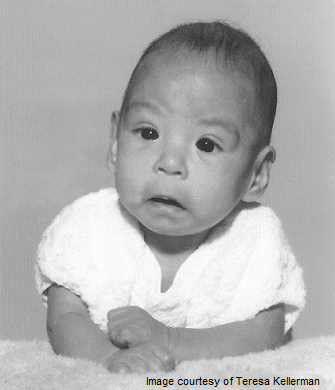 A woman presents to the hospital in labor. She states that she has not had any prenatal care. She delivers an infant of normal weight, but he has a smooth philtrum and his head is small. A photo of a similarly affected infant is shown.
A woman presents to the hospital in labor. She states that she has not had any prenatal care. She delivers an infant of normal weight, but he has a smooth philtrum and his head is small. A photo of a similarly affected infant is shown.
Which of the following exposures would most likely produce this clinical picture?
A. Drinking alcohol
B. Rubella infection
C. Smoking cigarettes
D. Strenuous exercise
E. Using cocaine
———————–
Want to know the ‘bottom line?’ Purchase a USMLE-Rx Subscription and get many more features, more questions, and passages from First Aid, including images, references, and other facts relevant to this question.
This practice question is an actual question from the USMLE-Rx Step 1 test bank. For more USMLE Step 1 prep, subscribe to our Flash Facts and Step 1 Express video series. Score the best deal on all three products with USMLE-Rx 360 Step 1.




I choose A.
A
A for Alcohol
A) Fetal Alcohol Syndrome
Same picture in First Aid
The correct answer is A. This infant has a smooth philtrum and a small head, which are hallmarks of fetal alcohol syndrome. Later in life, affected children can demonstrate delayed growth and attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Other abnormalities, such as shortened palpebral fissures and low-set ears, may also be seen, and cardiac and lung abnormalities may be present.
Cigarette exposure increases the risk of abruptio placentae, placenta previa, and other potentially fatal complications; it also results in low-birth weight, but generally not in physical deformities. Excessive exercise may lead to premature rupture of membranes, but not in physical abnormalities in the newborn. Intrauterine rubella infection may manifest with the classic triad of hearing loss, cataracts, and congenital heart disease, inconsistent with this newborn’s presentation. Cocaine use can lead to placental abruption and growth retardation, but does not generally result in physical deformities.
B is not correct. The classic findings in congenital rubella include sensorineural hearing loss, retinopathy, cataract, microphthalmia, and congenital heart disease (pulmonary artery stenosis, patent ductus arteriosus). Later manifestations include intellectual disability. This infant’s physical abnormalities are not suggestive of congenital rubella syndrome.
C is not correct. Smoking increases the risk of abruptio placentae, placenta previa, and other potentially fatal complications. Affected babies are often born underweight. The physical malformations seen in this infant are not classically seen in children of smokers.
D is not correct. Strenuous exercise may result in the premature rupture of membranes but is not known to cause physical malformations.
E is not correct. Cocaine use can lead to placental abruption and stillbirth/miscarriage. Growth retardation is commonly seen, as is preterm labor. The latter may be related to decreased blood flow to the fetus, as cocaine acts as a vasoconstrictor. This infant’s physical abnormalities are not characteristic of cocaine use during gestation.
Thank you for the explanation. It’s greatly appreciated.